The process of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) typically involves the following steps:
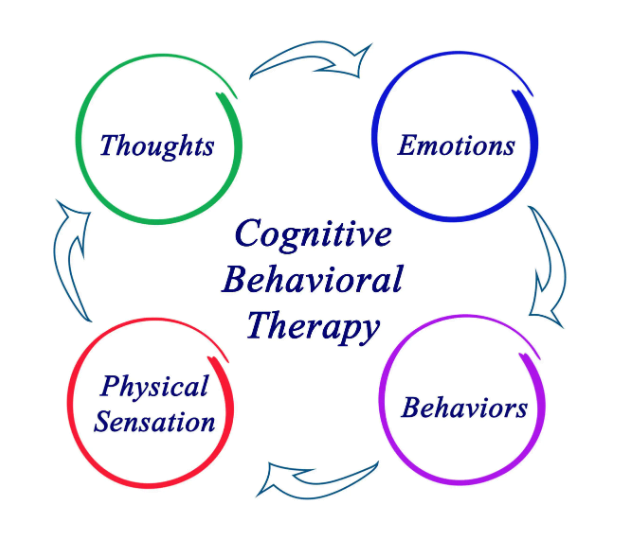
- Initial assessment: The therapist will assess the client’s current symptoms and concerns, as well as their current functioning and goals for therapy.
- Identifying negative thought patterns: The therapist will help the client identify negative thought patterns that may be contributing to their symptoms. This includes identifying automatic thoughts and beliefs that may be distorted or irrational.
- Examining the evidence: The therapist will help the client examine the evidence for and against their negative thoughts and beliefs, in order to challenge and modify them.
- Re-evaluating beliefs: The therapist will help the client re-evaluate their negative beliefs and replace them with more realistic and helpful beliefs.
- Changing behaviors: The therapist will help the client identify and change behaviors that may be maintaining their negative thoughts and beliefs. This may include exposure therapy or other behavioral techniques.
- Monitoring progress: The therapist will help the client track their progress and monitor their symptoms and behaviors over time. This will allow them to see the impact of the changes they have made and make any necessary adjustments.
- Termination: Once the client has reached their goals and is functioning at a satisfactory level, the therapist will help them prepare for termination of therapy

Advantages of Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- It focuses on present-moment problems and challenges, rather than past experiences.
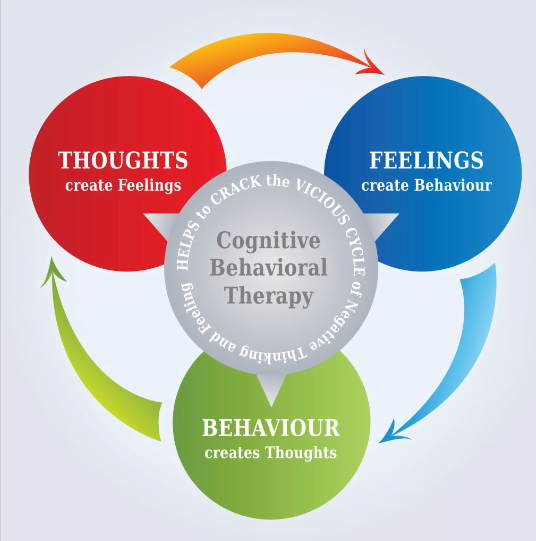
- It emphasizes the role of thoughts and beliefs in shaping emotions and behaviors.
- It teaches practical skills and strategies for managing symptoms and improving functioning.
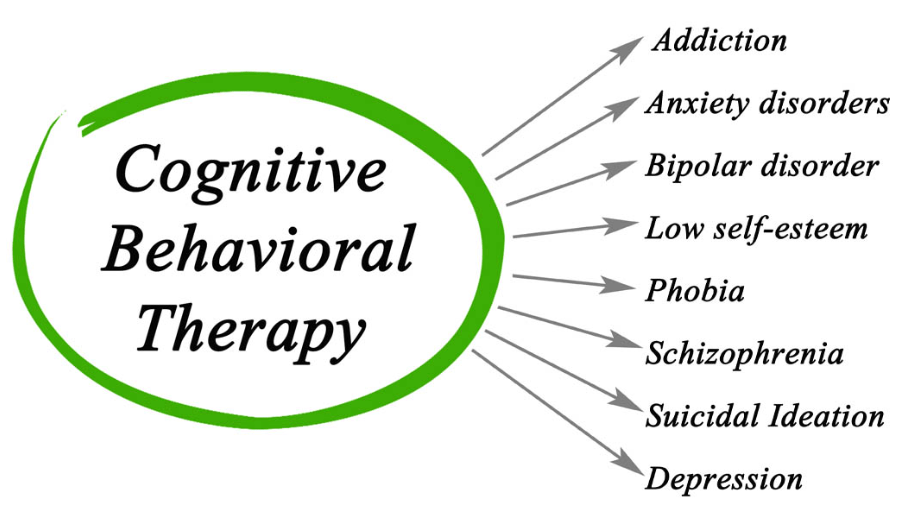
- It has a strong evidence base and has been shown to be effective for a wide range of mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and substance abuse.
- It can be short-term, typically lasting 12-20 sessions, making it a more time-efficient treatment option.
- It can be easily adapted to be delivered in a variety of settings, including individual therapy, group therapy, and online therapy.
- It promotes self-reliance and encourages individuals to take an active role in their own recovery process.
Disadvantages of Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
There are some disadvantages of Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for mental health in psychology:
- Time-consuming: CBT requires a significant time investment, as it typically involves weekly sessions with a therapist over a period of several months. This may not be feasible for some people with busy schedules or limited access to therapy.
- Limited flexibility: CBT is a structured form of therapy that focuses on specific goals and interventions. This can be inflexible for people with complex mental health issues that may require a more personalized approach.
- Requires effort: CBT requires active participation and effort from the individual seeking therapy. This may be difficult for some people who may not be ready or willing to work on their issues.
- Not suitable for everyone: CBT may not be suitable for everyone, as it may not address the underlying causes of some mental health issues. This can lead to a limited or incomplete treatment approach.
- Stigma: There is still a significant stigma surrounding mental health issues, which may discourage some people from seeking CBT or any form of therapy.
